Think Olympus only makes cameras?
Although compared with Canon and Nikon, Olympus has a smaller market share, it has up till now produced a great number of distinctive cameras which has won it many fans. For that reason, it is commonly thought of as a commercial camera manufacturer.
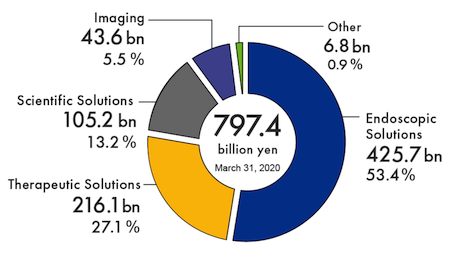
However, its main business is not in the audio-visual sector which deals with digital cameras and the like. It is in fact a global manufacturer of medical devices which account for 80% of its sales.
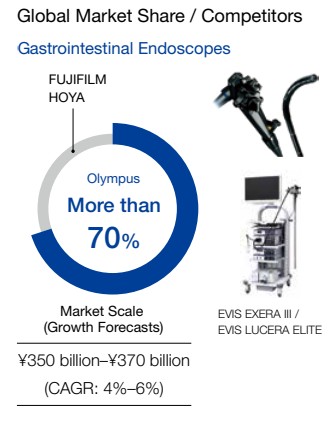
Above all, in the field of gastrointestinal endoscopes including gastroscopes and colonoscopes, it is the undisputed No. 1 manufacturer with over 70% of the world market share .
In this article we will look at the history of Olympus and introduce the latest AI technology that Olympus employs in its medical devices.
Founded with a microscope, and now a world leading manufacturer
True to its image as a camera manufacturer, Olympus has been developing optical equipment since the company was first established. It was founded in 1919 with the aim of developing a domestically produced microscope and launched the Asahi microscope on the market in 1920. At that time, the company name was Takachiho Seisakusho, but Olympus was registered as a trademark in 1921.
The development of cameras was relatively late, with the Zuiko lens and the Semi-Olympus camera being the first products released in 1936.
Now Olympus is the world’s leading manufacturer of biological microscopes and industrial endoscopes, with a 40% share of the market.
The first practical gastroscope was developed by Olympus
Olympus is not only the world’s top gastrointestinal endoscope manufacturer, but it was the first company in the world to develop a practical gastroscope. The company’s first gastroscope was the GT-I, which was developed as a prototype in 1950 and launched commercially in 1952 .
Since that time, Olympus has continued to produce cutting-edge gastrointestinal endoscopes and has maintained the world’s top market share.
AI diagnoses colonoscope images in real time
A gastrointestinal endoscope is a medical device that enables doctors to see, inspect and diagnose the condition of the stomach and intestines, and also to surgically remove any affected areas on the spot. Olympus has applied deep learning technology to these gastrointestinal endoscopes and added diagnostic support software called EndoBRAIN-EYE.
During an examination with the colonoscopy system EVIS LUCERA ELITE, this software analyzes images in real time, and when a suspected lesion is detected, it sends the doctor an on-screen alert.
The deep learning algorithm was trained with 3.95 million images obtained from endoscopic video recordings. As a result, in clinical performance trials it was able to accurately detect lesions with a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 89%.
This feature can help doctors avoid overlooking lesions during colon examinations. However, an area possibly affected by a lesion is not shown on the screen. The system simply emits a warning sound and displays an on-screen message that there is a possible lesion. This is perhaps due to the designers’ philosophy that the final diagnosis is down to the doctor.
EndoBRAIN-EYE was jointly developed by Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital, Nagoya University Graduate School, Cybernet Systems, and Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. Olympus will market EndoBRAIN-EYE in Japan.